Metabolic Syndrome (MES)
Are you suitable for bariatric surgery? | Benefits of Surgery | The vicious cycle of obesity |
Type II DM Control after Bariatric Surgery | Reduction of Cardiovascular Risk after Bariatric Surgery |
Metabolic Syndrome | FAQ
What is metabolic syndrome?

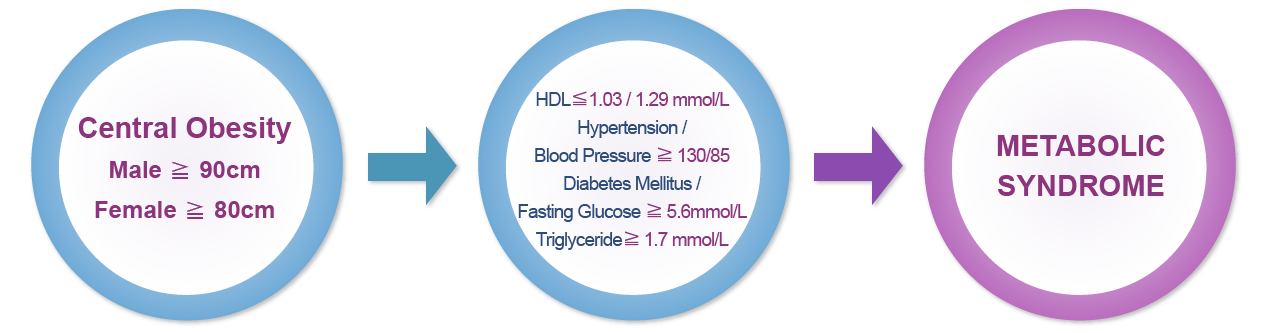
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), metabolic syndrome is a cluster of risk factors that contribute to heart attack, such as diabetes, increased fasting plasma glucose(>/= 5.6 mmol/L), abdominal obesity, high blood cholesterol (HDL /= 1.7mmol/L) and high blood pressure (>/= 130/85) [1] .
Central obesity, which is defined as having a waistline over 90cm in men and over 80 cm in women, is the proven marker for any future clinical events. It is estimated that about a quarter of the world’s population is suffering from metabolic syndrome and they are two to three times more likely to have a heart attack (acute myocardial infarction) or stroke compared to healthy individuals without the problem.
Furthermore, patients with metabolic syndrome are five times more likely to develop type 2 diabetes, in addition to 230 million diabetic patients worldwide who had already been diagnosed with the disease, which is also one of the top 5 leading cause of death in developed countries. This clustering of risk factors of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) is now considered as the driving force of the CVD epidemic.
Causes of Metabolic Syndrome
The underlying cause of this disease remains to be a challenge to scientists nowadays. However, insulin resistance and central obesity are considered as significant factors of metabolic syndrome.
Management of MES
Lifestyle modification, increased exercise level, dietary changes and medical therapy are commonly used and known to be effective in slightly overweight patients. However, these measures may not be as effective in severely obese patients (BMI over 30). As such, bariatric surgery was known to be the most effective and long-lasting means for managing patients with severe obesity currently, which has growing popularity in western countries and are recently introduced in Asian countries.
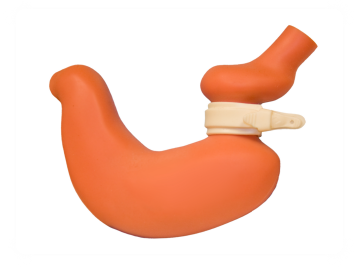
Bariatric surgery as treatment options in Hong Kong [2] In a study conducted by The Chinese University of Hong Kong, in a total of 502 patients evaluated, 82% of them (n=412) were classified as severely obese with BMI over 30 and 67% of them were diagnosed with metabolic syndrome, which the prevalence is four time greater than the general population.

116 patients with severe obesity underwent various bariatric surgeries, including intragastric balloon, laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding and laparoscopic gastric bypass operation. 99.1% of the patients showed significant improvement of the metabolic syndrome and 61.2% of them even had the syndrome resolved. The surgeries were performed in approach with little complications occurred and zero mortality, which proved the feasibility and efficacy of bariatric surgery in treating MES among severely obese Chinese patients.
As shown in the study, the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in severely obese Chinese patients in Hong Kong is fourfold compared with the general public, plus the application of bariatric surgery provides these patients an effective and potential curative option towards metabolic syndrome, as well as preventing multiple diseases in the future as a result of MES.
[1] IDF, 2006
[2] CUHK 2007


